ChIP-seq preprocessing
Overview
Teaching: 0 min
Exercises: 0 minQuestions
How to align ChIP-seq fastq files?
How do you analyze the ChIP-seq data?
Objectives
Use bowtie1 for mapping reads
Use MACS for calling peaks
get the raw fastq data
ssh test2017@139.52.107.59
# go to your home directory
cd ~
# make a new directory
mkdir ChIP-seq
## go insde
cd ChIP-seq
## copy the fastqs
cp /course/ChIP-seq_lab/fastqs/*fq .
## have a look, you should see two fastqs in the folder
ls
quality control
skip it
fastqc IMR90_H3K4me3_chr6.fq
fastqc IMR90_Input_chr6.fq
Alignment
I will walk through you for the H3K4me3 IP fastq file.
full path
bowtie2: /bioinfo/bowtie2/bowtie2
samtools path: /bioinfo/samtools
bedtools intersectBed : /bioinfo/intersectBed
Note: replace all the commands below with the full path of the program.
step1:
# use only 1 cpu
bowtie2 -x /bioinfo/bowtie2/hg19/hg19 -U IMR90_H3K4me3_chr6.fq --thread 1 -S IMR90_H3K4me3_chr6.sam
reads processed: 247026
reads with at least one reported alignment: 246922 (99.96%)
reads that failed to align: 46 (0.02%)
reads with alignments suppressed due to -m: 58 (0.02%)
Reported 246922 alignments to 1 output stream(s)
real 1m30.854s
user 1m28.444s
sys 0m1.181s
step2:
## conver the sam to bam, bam is a binary form of sam
samtools view -Sb IMR90_H3K4me3_chr6.sam > IMR90_H3K4me3_chr6.bam
step3:
## remove duplicates (there is no duplicates in this example)
## remove duplicates that have exactly the same start and end coordinates. most likely
## due to PCR over-amplification
## -s for single end; -S for paired-end
samtools rmdup -s IMR90_H3K4me3_chr6.bam IMR90_H3K4me3_chr6_rmdup.bam
step4:
## sort the bam by coordinates
samtools sort -m 2G IMR90_H3K4me3_chr6_rmdup.bam IMR90_H3K4me3_chr6_rmdup.sorted
## index the bam
samtools index IMR90_H3K4me3_chr6_rmdup.sorted.bam
# IMR90_H3K4me3_chr6_rmdup.sorted.bam index will be created.
step5:
# check again
ls
## view the alignments
samtools view -h IMR90_H3K4me3_chr6_rmdup.sorted.bam | less -S
get statistics of the bam file
samtools flagstat IMR90_H3K4me3_chr6.bam
samtools flagstat IMR90_H3K4me3_chr6_rmdup.sorted.bam
your turn to align the Input file
Exercise
How do you align the Input fastq file?
Solution
bowtie2 -x /bioinfo/bowtie2/hg19/hg19 -U IMR90_Input_chr6.fq --thread 1 -S IMR90_Input_chr6.sam samtools view -Sb IMR90_Input_chr6.sam > IMR90_Input_chr6.bam samtools rmdup -s IMR90_Input_chr6.bam IMR90_Input_chr6_rmdup.bam samtools sort -m 2G IMR90_Input_chr6_rmdup.bam IMR90_Input_chr6_rmdup.sorted samtools index IMR90_Input_chr6_rmdup.sorted.bam
chain the steps by a pipe
The above step by step process is OK, but it generates too many intermediate files.
For the power users, we use | pipe to chain all the step together:
DO NOT RUN THIS only for power users.
bowtie2 -x /course/ChIPseq_lab/bowtie_index/hg19 -U IMR90_H3K4me3_chr6.fq -S | samtools view -Sb -F 4 - | samtools rmdup -s /dev/stdin /dev/stdout | samtools sort -m 2G - IMR90_H3K4me3_chr6_rmdup.sorted
samtools index IMR90_H3K4me3_chr6_rmdup.sorted.bam
bowtie2 -x /course/ChIPseq_lab/bowtie_index/hg19 -U IMR90_Input_chr6.fq -S | samtools view -Sb -F 4 - | samtools rmdup -s /dev/stdin /dev/stdout | samtools sort -m 2G - IMR90_Input_chr6_rmdup.sorted
samtools index IMR90_Input_chr6_rmdup.sorted.bam
Peak calling
we will use MACS for peak calling, one of the most popular callers.
Step1: peak calling without Input control:
## ~ 10mins to finish
macs -t IMR90_H3K4me3_chr6_rmdup.sorted.bam -f BAM -g hs --outdir peaks -n IMR90_H3K4me3_no_Input -p 1e-5 --bdg
Step2: peak calling with Input control
macs -t IMR90_H3K4me3_chr6_rmdup.sorted.bam -c IMR90_Input_chr6_rmdup.sorted.bam -f BAM -g hs --outdir peaks -n IMR90_H3K4me3_with_Input -p 1e-5 --bdg
bedtools to compare the peak sets
## how many peaks?
cd peaks
wc -l IMR90_H3K4me3_no_Input_peaks.bed
wc -l IMR90_H3K4me3_with_Input_peaks.bed
## what are the unique peaks that are called without Input?
/bioinfo/intersectBed -a IMR90_H3K4me3_no_Input_peaks.bed -b IMR90_H3K4me3_with_Input_peaks.bed -v > potential_artifact_peaks.bed
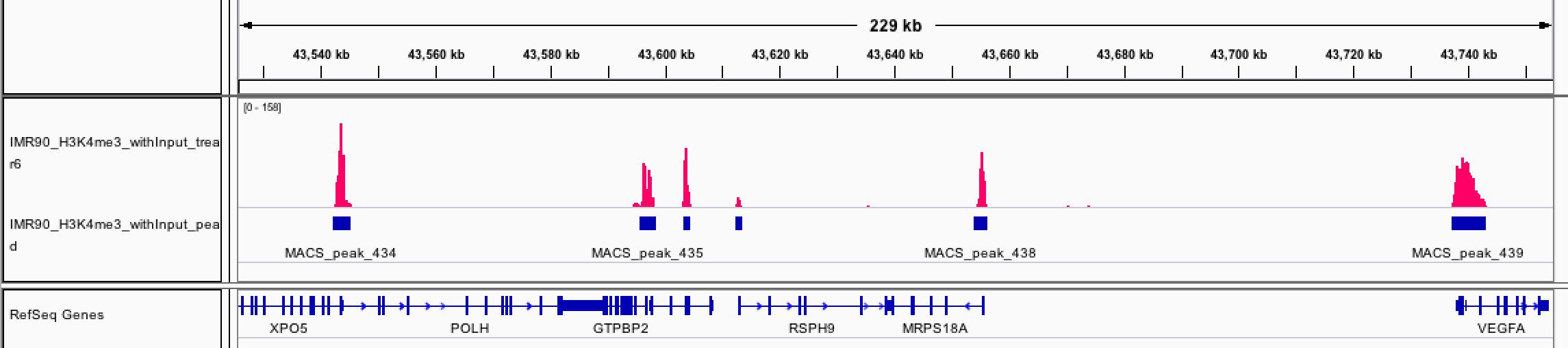
visualize in IGV
peaks and bedgraphs are the two files that you will need to download to your local computer for IGV visualization.
go to your own local computer
mkdir ChIP_seq_lab_results
cd ChIP_seq_lab_results
rsync -avhP username@139.52.107.59:~/ChIP-seq/peaks .
load the bedgraph file for chr6 and the bed file for visualization. go to chromosome 6! we only have data there.
e.g.
Screenshot of VEGFA and nearby loci:
Key Points
Input control is critical in controlling false postive peaks
bedgraph is the raw signal file for visualizing read density